Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting
Comparison Updated on : December 31, 2025Every business strives to have a robust website. But before developing a good website, you must look for top-notch hosting services to store your website’s data and services. The most popular ones are cloud hosting and web hosting.
Both hosting services have benefits and challenges. Therefore, let’s examine the detailed comparison of cloud hosting vs web hosting.
Overview of Cloud Hosting
Unlike traditional web hosting, a cloud hosting service runs on several network servers. Therefore, your website can utilize resources from different servers within the same network instead of a single server.
This flexible hosting strategy allows your website to evolve or shrink as required. For instance, if your website is experiencing high traffic, it can take extra resources from other servers to manage the load. Therefore, cloud hosting provides your website with scalability and flexibility to suit its current situation and requirements.
Cloud hosting options include:
1. Software as a Service (SaaS): It is the standard option that most businesses prefer for cloud hosting services. This option includes third-party vendors that use the Internet to deliver apps to their end users.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): This includes a cloud hosting option that offers a cloud component to specific software. It is mainly used for applications.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS allows you to overcome the complexity of purchasing and managing a single physical server and data center infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Hosting
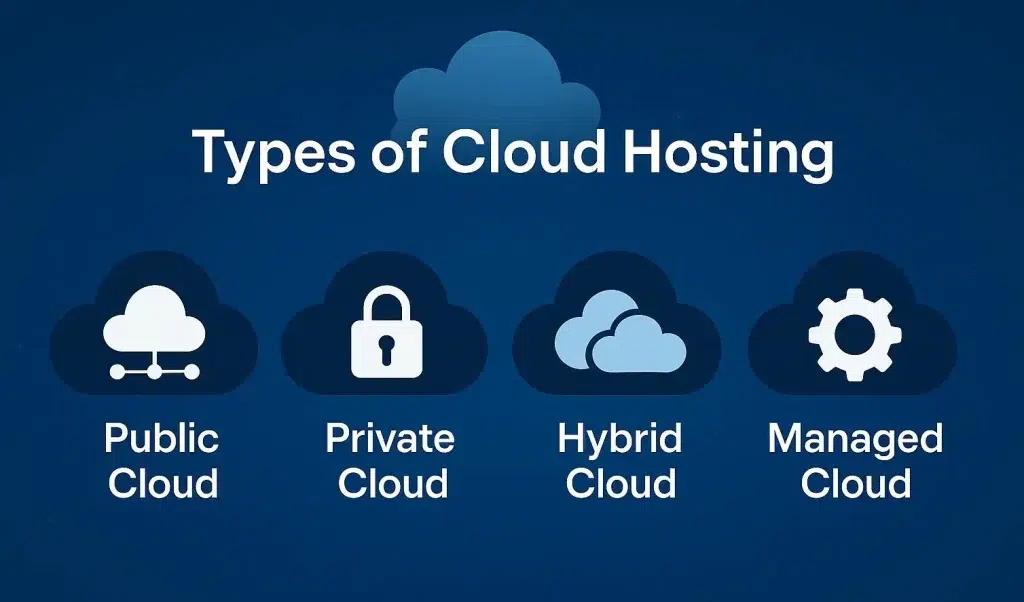
1. Public Cloud: A cloud environment where services and infrastructure are shared between multiple users (tenants). It is owned and operated by third-party providers like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure.
2. Private Cloud: A cloud infrastructure dedicated solely to one organization. It can be hosted on-site or by a third-party provider, but remains exclusive to a single client.
3. Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private cloud infrastructures that work together, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
4. Managed Cloud: A cloud solution is one where a third-party provider manages cloud infrastructure, services, and technical support on behalf of the user.
Cloud Hosting Stats
- The Hosting Segment of the cloud industry’s revenue is estimated to reach $12B in 2025.
- Roughly 7.2 million websites use Cloudways cloud hosting.
- Basic cloud hosting costs around $8.47 per month.
- Most people use 36 cloud-based services every day.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Scalability and Flexibility. | Managing a cloud hosting environment requires technical knowledge. |
| Uptime and Reliability. | Cloud hosting can be expensive. |
| Cost Efficiency. | Restricted control over personalization. |
Overview of Web Hosting
In simple terms, web hosting is a service that stores your web application or website and makes it easily accessible across different devices like mobiles, tablets, and desktops. Any web application or website is mainly made of many files, like videos, text, images, and code, that you must store on special computers called servers.
Web hosting services are responsible for configuring, maintaining, and operating physical servers on which you can store your files. Website and web application hosting services offer additional support, such as website backup, security, and performance.
Types of Web Hosting
1. Shared Hosting: Shared hosting is a more cost-effective option for beginners. This method is best for newcomers and small websites.
2. VPS Hosting: VPS hosting divides a physical server into several virtual servers. Each virtual private server acts freely. This provides more control and dedicated resources than shared hosting.
3. Dedicated Hosting: You can access the physical server and resources in dedicated hosting. You don’t need to share the server with any other organization. It gives you complete control over the hardware and software server components.
4. Managed Hosting: Managed hosting mainly refers to managed services for apps like WordPress, where the hosting provider manages all the tasks, including security, performance, and backup services.
5. Colocation Hosting: Instead of keeping your servers in-house or at a private data centre, you may “co-locate” your equipment by renting space in a colocation centre. The centre will offer your server’s bandwidth, power, IP address, and cooling systems.
6. Reseller Hosting: As the name suggests, reseller hosting allows you to resell hosting services. You can purchase the hosting services and then resell them to others.
7. Hosting for WordPress: Hosting for WordPress is particularly optimized for WordPress websites. It provides features and resources that are personalized to the WordPress platform.
Web Hosting Stats
- The web hosting market is projected to reach $192.85bn in 2026.
- The average spend per employee in the web hosting market is expected to reach $53.68.
- There are over 330,000 web hosting providers globally.
- The United States generates the highest revenue in the web hosting market.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| Easy to set up and manage. | Dedicated hosting can be expensive. |
| If you opt for VPS, you can get more control over server configurations. | Some hosting types lack personalization abilities. |
| Maximum security and performance. | Limited backend controls. |
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Hosting | Web Hosting |
| Infrastructure | It utilizes a network server spread across different geographies. | It is restricted to a single server or group of servers at one location. |
| Price | Most of the cloud hosting providers offer a pay-as-you-go model. | Primarily involved fixed monthly prices. |
| Security | Strong security measures, including SSL, firewalls, identity management, and data encryption. | High security offers dedicated servers for isolation. |
| Performance | High performance comes with extra resources during peak times. | Consistent performance but may face limitations during traffic spikes. |
| Management | Cloud hosting providers manage servers. | Managed hosting handles all the operating, including server management & OS updates. |
| Customization | Allows greater infrastructure personalization for customized server performance & storage. | Limited customization is due to the constraints of operating on a single server. |
| Use Cases | Best for business websites with fluctuating traffic. | Best for high-traffic websites. |
Is Cloud hosting a type of web hosting?
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting. Traditional web hosting involves services hosted on a single server, while cloud hosting particularly refers to web hosting services that use cloud technology to offer resources and servers.
Think of cloud hosting as using ride-sharing apps (like Uber or Lyft) instead of owning a single car.
You’re stuck with that one vehicle when you own a car (like traditional web hosting). If it breaks down or isn’t powerful enough, you’re in trouble.
But with cloud hosting, it’s like using a ride-sharing app. Whenever you need a ride, you get one. If you need a bigger car, it shows up. If one car isn’t available, another one is. The system is flexible, reliable, and adapts to your needs.
In the same way, cloud hosting uses a network of servers, not just one. So, if your website suddenly gets a lot of visitors or needs more resources, the cloud adjusts automatically to keep it running smoothly.
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Performance
1. Cloud hosting
Cloud hosting means you are less dependent on one server as your website is hosted across several servers. Therefore, if one server has a problem, the other responds immediately to continue delivering your website. This results in better performance stability with faster loading times. In addition, if there’s a sudden spike in traffic to your website, the cloud can immediately switch the resources as per requirements.
2. Web hosting:
Unlike cloud hosting, it doesn’t have multiple servers; it is hosted on a single server. To help you understand better, imagine web hosting like a single-lane bridge. If that one lane gets blocked, or let’s assume a car breaks down, traffic grinds to a halt for everyone. In contrast, cloud hosting is like a multi-lane highway; vehicles merge into the other lanes and keep moving if one lane is closed for an accident or maintenance.
Therefore, traditional web hosting is a gamble when you look for performance. If your website is not hosted on a good server that goes down frequently, so does its performance. Your site’s performance depends on how many other websites are shared on the server.
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Server Infrastructure
1. Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting includes virtualization across distributed server networks. The infrastructure provides physical hardware for pooling resources and virtual instances from different servers for dynamic allocation. This distributed architecture has multiple geographies, offering geographic redundancy and flexible resource provisioning depending on real-time demands.
2. Web Hosting
Web hosting runs on dedicated physical servers within particular data centers. Users get full hardware access and top-notch usage of fixed RAM, CPU, and storage allocations, allowing predictable performance and complete infrastructure control. The hardware architecture provides direct access to computing resources without requiring virtualization layers.
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Budget
1. Cloud Hosting: Most cloud hosting services offer a pay-as-you-go model, which means you pay for the resources you use.
2. Web Hosting: Most web hosting plans come with fixed resources. If website traffic spikes and you need more resources, upgrade your plan or buy an add-on service.
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Security Measures
1. Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting comes with more top-notch security measures. As your data is distributed across a different network of servers, it can be safer from physical threats like hardware failure. Also, most cloud hosting providers have robust security features, including user authentication and data encryption.
2. Web Hosting
In web hosting, your security depends on the hosting provider you select. Most web hosting providers offer security measures like malware detection, firewalls, and regular updates to safeguard your website from hackers.
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Which One to Choose?
Choose Cloud Hosting if:
- If you need powerful processing for high traffic volume.
- If you are looking for a scalable and cost-effective solution.
- If you expect growth and need more than web hosting.
- If your business can’t afford downtime.
Choose Web Hosting if:
- If your website traffic doesn’t fluctuate.
- If you don’t need advanced features.
- If you know how much RAM, CPU, and disk you need.
- If you prefer all-in-one managed hosting packages, updates, security patches, and more.
Cloud Hosting vs Web Hosting: Final Verdict
Traditional web hosting continues to be a dependable, cost-effective option. It’s ideal for small-scale projects, personal portfolios, or startups with limited traffic and resources. It’s straightforward, budget-friendly, and easy to manage.
However, when growth is on the horizon and digital demands evolve, cloud hosting emerges as a smarter investment. It is a powerful tool with dynamic scalability, superior uptime, and robust performance infrastructure. Therefore, it’s not just about hosting your website; it’s about hosting your potential. Choose wisely depending on your vision.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs
Q1. Which is better, web hosting or cloud hosting?
Ans. Traditional web hosting is simpler and often cheaper for small, predictable sites. Cloud hosting offers greater flexibility and reliability by distributing resources across multiple servers. The best choice depends on your site’s traffic patterns, budget, and growth plans.
Q2. Is cloud hosting a type of web hosting?
Ans. Yes, cloud hosting is one of several web-hosting models. It delivers your site from virtual servers that draw on a pooled network of physical machines. This contrasts with traditional hosting, which ties you to a single server.
Q3. Which hosting type offers better scalability?
Ans. Cloud hosting scales automatically by adding or removing resources as needed. Traditional hosting requires manual upgrades or migrations to handle the increased load. For rapid growth or traffic spikes, cloud hosting is far more flexible.
Q4. What types of websites benefit most from cloud hosting?
Ans. Sites with fluctuating or high traffic, like e-commerce stores during sales, SaaS apps, and media-heavy portals, gain the most. Global audiences benefit from spinning up servers in different regions for low latency. Data-intensive or burst-computer workloads also thrive in the cloud.
Q5. Which hosting option provides better security?
Ans. Cloud hosting often includes managed security features such as WAFs, DDoS protection, and automated patching. Shared or basic traditional hosting can expose you to neighbor-site vulnerabilities. If strict compliance or isolation is required, cloud environments offer stronger controls.
Q6. Which hosting is better for a small business website?
Ans. Traditional shared hosting is sufficient for a simple brochure site or blog with steady, low traffic, and tight budgets. A basic cloud plan is a good investment if you anticipate growth, seasonal spikes, or need more control. Choose based on your projected needs and cost priorities.
Q7. Is cloud hosting suitable for e-commerce websites?
Ans. Yes, Cloud hosting is suitable for e-commerce websites. It ensures that your store stays online during peak sale hours. It supports PCI-compliant managed services and scales to manage large order volumes. CPU, RAM, storage, and networking on demand. A web server is software (like Apache or Nginx) that delivers web pages and assets over HTTP(S). You can run a web server on a cloud server, VPS, or physical machine.




