
How Does The Performance of Your Website Change With HTTP VS HTTPS?
Security Published on Date: September 30th 2021Table of Contents
HTTP vs HTTPS: A Brief Introduction
HTTPS is essentially HTTP with added security measures. The key distinction is that HTTPS employs TLS (or SSL) to encrypt regular HTTP interactions, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the exchanged data. It also utilizes digital signatures to verify the authenticity of both the requests and responses.
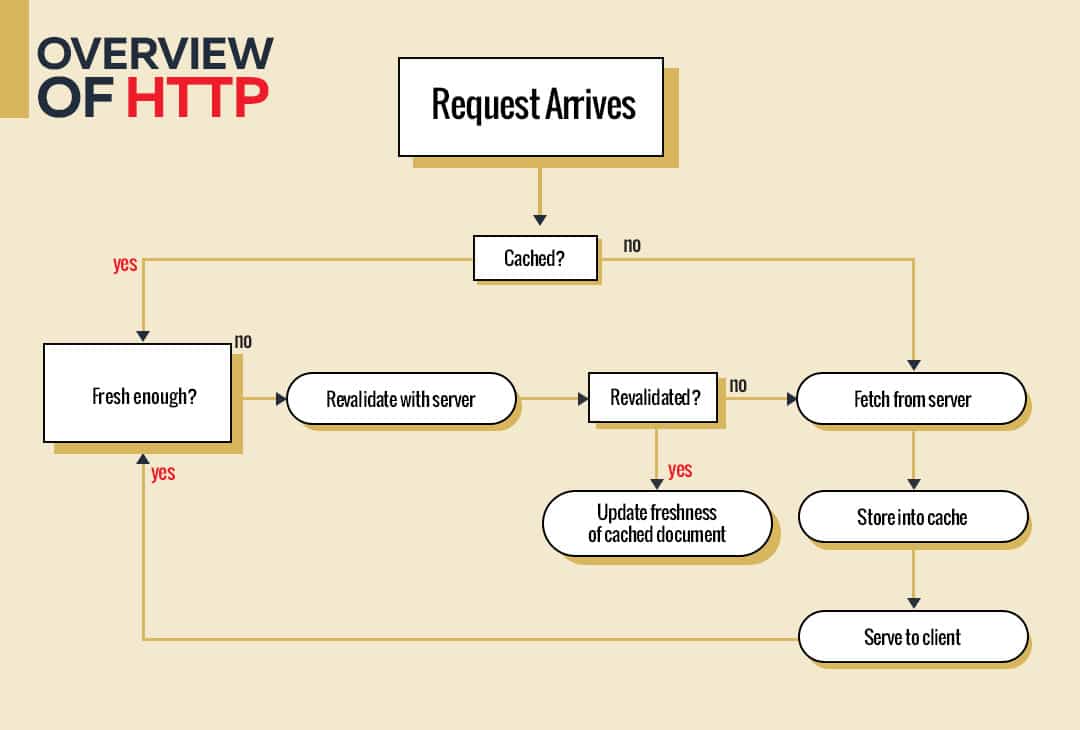
Certainly, in the ongoing comparison between HTTPS and HTTP, it becomes evident that HTTPS serves as a fortified iteration of the preexisting HTTP protocol. Moreover, a comprehensive examination reveals a spectrum of additional functionalities that demarcate these two protocols. Let us embark on a comprehensive overview of both, thereby elucidating their distinctions and attributes.
What is HTTP?
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is the protocol that facilitates interaction among distinct systems, allowing the exchange of information and data across a network.
HTTP serves as the primary method for transferring data from web pages over a network. Web pages are stored on servers and are delivered to client computers upon user request. Due to its ability to provide on-demand connections to initiating browsers, HTTP is characterized as a stateless system.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS stands for (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) and is an encrypted variant of HTTP, the most used protocol for sending data over the Internet. Any website that has a lock icon in the address bar is using HTTPS. Around 83.7% website use HTTPS for their online site security (Source:w3techs.com )
How HTTPS Works?
The SSL certificate encrypts users’ data on the site, effectively converting it to a code. Even if a third-party attacker were to steal the data sent between the sender and the receiver, the encryption would prevent them from comprehending it.
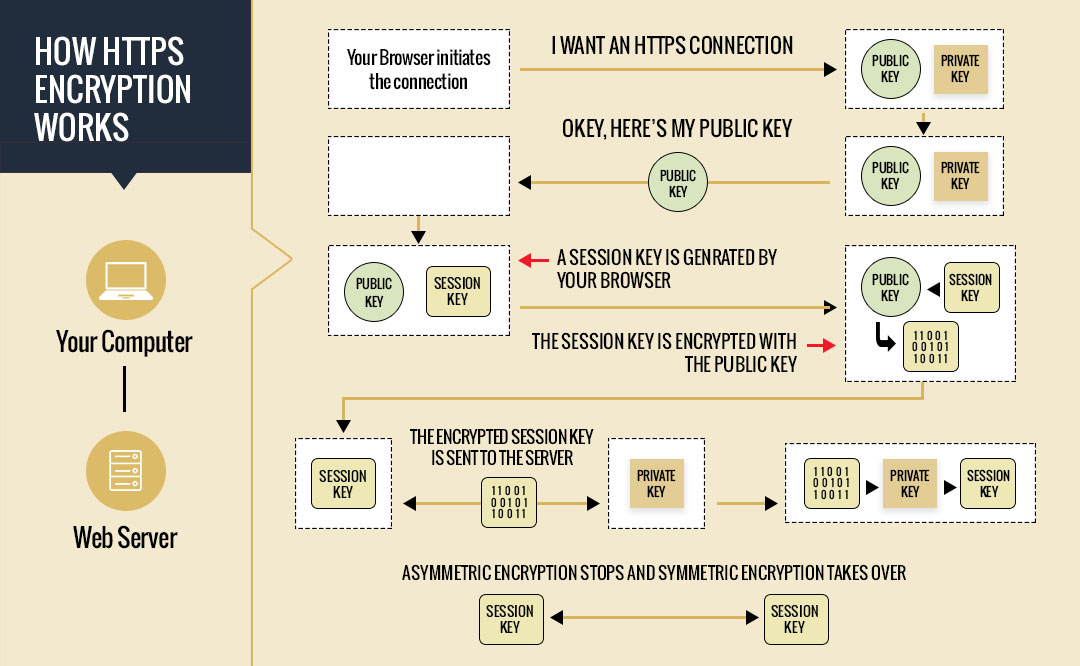
Furthermore, HTTPS adds an extra layer of security by using the TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol. TLS helps ensure data integrity by preventing data from being changed or damaged during transmission. It also provides authentication by proving to your users that they connect with the correct website.
Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS: Weighing The Perks
Understanding the Terms Better
Imagine passing a written message to your final recipient through a group of people. Now if the letter is written in a language readable by everyone along the way, the recipients might benefit, misuse or take advantage of the information. How they use it will be beyond your control. This describes the working of HTTP.
Imagine sending the same message in code language that only the final recipient will understand. Even the thought feels safer, right? This is how HTTPS encrypts the data and information that you share online.
While you might have come across the main difference as HTTP vs HTTPS security, the list goes far beyond including HTTP vs HTTPS SEO and performance. This is a digitally signed document and does not require a physical signature. Let us begin by exploring the advantages of HTTP, followed by the ones in the HTTPS basket.
Advantages of HTTP
- Can Be Accessed Quickly
- It’s Flexible
- Advanced Addressing Mechanism
- Easy To Program
- Enables A Secure Transmission
- Amazing Search Capabilities
- Speedy Transmission
Here are seven perks of using HyperText Transfer Protocol:
1. Can Be Accessed Quickly
Upon the initial loading of a website, all HTTP pages are stored in the page cache, a specific form of internet cache. Consequently, during subsequent page reloads, the content loads swiftly due to this cached data.
2. It’s Flexible
HTTP possesses the capacity to download extensions or plugins, enabling it to present necessary data whenever an application seeks additional functionalities. This characteristic guaranteed adaptability. Prime illustrations of this phenomenon include Flash players and Acrobat Reader.
3. Advanced Addressing Mechanism
The HTTP protocol employs an advanced addressing mechanism that assigns IP addresses to familiar names, facilitating their straightforward identification on the Internet. In contrast to the traditional approach of utilizing a sequence of digits following an IP address, this method allows the public to interact with the internet in a more accessible manner.
4. Easy To Program
HTTP employs plain text, simplifying comprehension and implementation compared to protocols that depend on lookup codes. Information is conveyed through lines of text rather than variables, resulting in a straightforward and efficient procedure.
5. Enables A Secure Transmission
Under the framework of HTTP 1.0, individual files are obtained one by one and subsequently terminated after download. This approach of establishing discrete connections for each element of a web page minimizes the risk of interception during data transmission. To enhance security, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) employs encryption to safeguard HTTP transactions.
6. Amazing Search Capabilities
While functioning as a fundamental communication protocol, HTTP provides the capability to perform a database search through a singular request. This empowers the protocol to conduct SQL searches and furnish outcomes that can be conveniently organized on an HTML page.
7. Speedy Transmission
A Web page is made up of a variety of components, such as text and pictures. Each component needs a varying quantity of storage and download resources. HTTP allows several connections to download different components at the same time, which speeds up the transmission. Each component is also given its own file type, allowing the receiving computer to process them more quickly and effectively.
Advantages of HTTPS
- Helps You Build Trust
- Helps Boost Website Rankings ( SEO)
- Provides Impeccable Security
- Helps Preserve Referrer Data (SEO)
- Qualifies You For AMP Pages
Here are the five perks of using HTTPS which helps with SEO and other things:
1. Helps You Build Trust
An HTTPS site encrypts all communication keeping visitors’ sensitive information protected. By keeping passwords, credit card information, browsing history, etc., safe – HTTPS helps you build trust in visitors. It will help you establish a healthy image and authenticity if you assure people that their information is protected while they browse your website.
2. Helps Boost Website Rankings ( SEO)
As mentioned earlier, Google has encouraged HTTPS over HTTP by incentivizing the change through a minor hike in rankings. The advantages of HTTPS over HTTP is it can significantly help enhance your website’s rankings over time, as users will be more inclined to browse through secure sites.
3. Provides Impeccable Security
This is an obvious one. HTTPS was introduced to make websites more secure and safe for users. In the case of HTTPS, the SSL/TLS certificate protects data while it is being transmitted between your website and the client.
Furthermore, implementing a certificate to authenticate your identity will assure your site’s legitimacy, allowing consumers to believe that their data is safe. This distinguishes your website from those of phishing sites. This factor also helps in SEO as users will want to stick longer on a site that seems safe and authentic.
4. Helps Preserve Referrer Data (SEO)
Using an HTTPS site improves the effectiveness of Google Analytics. This is because HTTPS sites keep the security details of the website that referred to you, but HTTP sites do not. Referral sources will display as “direct traffic” on HTTP sites. This alone offers HTTPS a significant SEO benefit.
5. Qualifies You For AMP Pages
Google introduced AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) to load information on mobile devices more quickly. AMP content is prominently displayed in Google’s SERPs to provide a better mobile experience for smartphone and tablet users.
HTTP vs HTTPS Difference: What Are The Downsides?
As fruitful as both systems are, HTTP and HTTPS have their disadvantages. Let us delve into http and http difference individually in the section below.

3 Disadvantages Of Implementing Hypertext Transfer Protocol
1. Lack Of Security
The most significant disadvantage of an HTTP website is that it does not provide secure communication as the data is not encrypted and is transmitted in plaintext format. Your data can be hacked, stolen, or altered by intruders when utilizing an HTTP site.
2. Lack Of Privacy
There is one big drawback to using an HTTP connection: data sent via an HTTP connection is not encrypted, putting you in danger of third-party hackers obtaining your data. If you are on an HTTP page, any credit card details or sensitive information should not be provided since any information transferred over this network via HTTP is not private.
3. Does Not Support IoT Devices
HTTP consumes more system resources, resulting in higher power usage. As a result, HTTP is not compatible with IoT devices nowadays since they incorporate wireless sensor networks.
3 Disadvantages Of Implementing HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure
1. Can Prove Uneconomical
You’ll need to get an SSL certificate after you switch to HTTPS. Despite the fact that many SSL certificates are provided by the website hosting provider, they must be updated annually for a charge – which can be a bit pricey.
Although there are ways to obtain a free SSL certificate, you might want to check the paid options and ensure security.
2. May Render Inaccessible
Some firewalls and proxy systems prevent HTTPS sites from being accessed. This can be both deliberate and unintentional. In the instance of a non-intentional breach, the administrators may have neglected to enable HTTPS access. This can sometimes be done on purpose as a security precaution.
3. Causes Problems In Catching
In HTTPS, some items will have caching issues. The public will not cache those that have already been cached, so ISPs will not be able to cache encrypted material. These kinds of issues are more probable on sites that have a large number of visitors. Increased bandwidth mitigates these difficulties.
HTTP vs HTTPS – A Word Of Advice For Website Owners
1. Traffic
As a website owner, you value website traffic the most. What if one of these protocols can help you get more relevant traffic? HTTPS, by virtue of its secure nature, attracts more traffic by performing better. This argument is also supported by Google. Thus, you are likely to get better google analytics results if your website starts with HTTPS.
2. Trust
When someone visits your website, the most crucial thing for you to do is to make sure they trust your website and feel secure. A trustworthy website might mean more traction, hence, more business. While the quality of your offerings is important, inculcating a sense of security in your users is even more important.
3. Payments
If you are paying for something online, pause! First, make sure that the web address says “HTTPS”. If it doesn’t we highly discourage you to share any of your credit/debit card or net banking information. The simple reason is that your personal information can be compromised, even if your transaction goes through.
4. Impulse Clicks
More internet adoption also means more cybercrime. Sometimes, you click on something fishy by accident. Can’t blame you, the hackers make things look highly genuine. Damage can still be controlled as long as you don’t share your personal information. As a thumb rule, no sharing of sensitive information if the website doesn’t feel secure.
Interesting Facts Impacting HTTP vs HTTPS
1. HTTP/2
HTTP/2 is an improved version of HTTP that allows sending more than one file at the same time – a term is commonly known as multiplexing. Additionally, HTTP/2 encrypts data just like HTTPS. Hence, HTTP/2 is definitely an improved version of HTTP.
The catch here is that HTTP/2 only functions over a secure encrypted connection such as HTTPS.
2. Relevance To Context
If you are mostly concerned about your landing pages’ Google rankings and your website’s performance in Google analytics, moving to HTTPS is only the first step.
In the future what’ll matter the most is how relevant your content is to the context. There are multiple tools that can help you prepare better.
3. Stats About HTTP vs HTTPS
Majority of the online buyers don’t complete their online purchase if the website is not secure. So an increasing number of websites are moving to HTTPS to offer a more secure experience.
Convinced that you need to move your HTTP to HTTPS, but don’t know how?
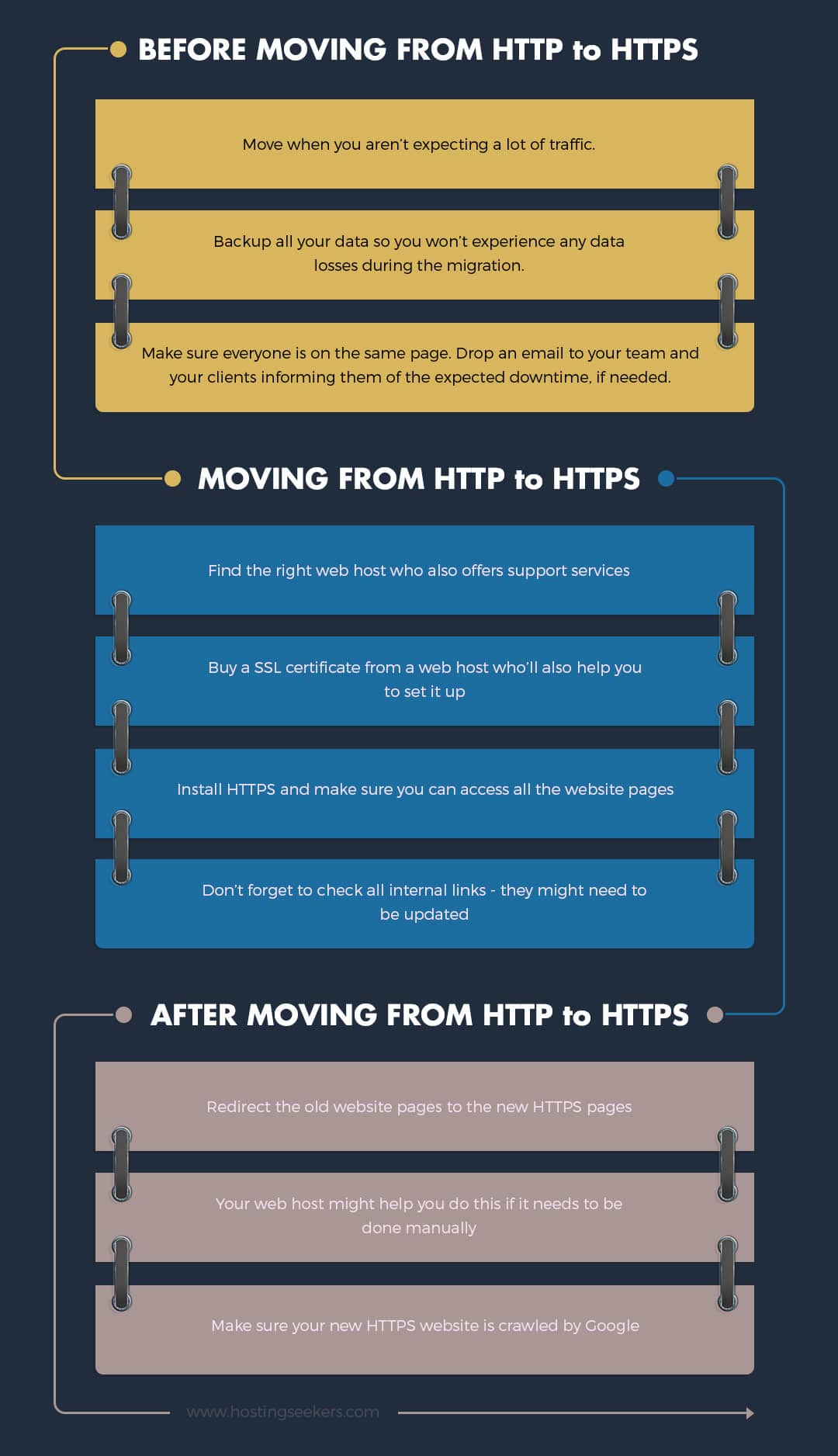
Impact On SEO When Changing From HTTP To HTTPS
As per Google’s transparency report released in January 2021, more than 80% of the websites opened in Chrome used HTTPS. This is a big achievement and reflects the widespread adoption of HTTPS by an increasing number of businesses. The non-adoption of HTTPS can impact your website negatively.
Make sure Google crawls your website once you move to HTTPS, and add 301 redirections, update sitemaps, and revise robots.txt. If everything is in place, you can expect the following impact on SEO when changing from HTTP to HTTPS:
1. Better Ranking
HTTPS helps visitors to feel secure, so they are more likely to click on your website. You’ll reach a wider set of audience who’ll find your information relevant. This in turn, increases the ranking of your website in the long term.
2. Increased Traffic
You can reach a wider audience who will trust the security of your website, so the traffic on your website will increase.
3. Higher Conversion Rate
Increased traffic increases your chances of a higher rate of conversion. More website visitors will stay on your page longer. In the end, it is a numbers game. If more people stay on the website longer, the higher their chances of conversion.
HTTP vs HTTPS: Our Verdict
Knowing the roles, advantages, and disadvantages of HTTPS vs HTTP, we can make a fair assumption about which option is best for your website. HTTPS seems like a more reasonable choice in today’s data-driven and SEO-dominated world. Moreover, It also a world of hackers and intruders, so security and privacy have to be of utmost importance.
For a variety of reasons, you want your website to be safe. Not only will you want to safeguard potentially sensitive information, but you’ll also want to ensure that your visitors are at ease when exploring your site. This is where HTTPS helps.
Now coming to HTTPS vs HTTP SEO aspects:
HTTPS has a significantly positive impact on SEO. This helps your website generate traffic, gather leads, and place yourself on the map.
HTTPS is a secure and authentic mechanism for your website, and these days, the most needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is HTTP and HTTPS?
A. HTTP is a protocol for exchanging data between a web server and a client. HTTPS is an encrypted variant of HTTP that exchanges data over the internet securely.
Q. Why is HTTP not secure?
A. The internet does not encrypt the data exchanged over HTTP. That’s why it is relatively less secure as compared to HTTPS.
Q. Why do we use HTTPS instead of HTTP?
A. HTTPS ensures the security of information exchanged between the web server and the client. We prefer HTTPS instead of HTTP. Some web browsers also prefer HTTPS and thus using HTTPS can influence your SEO and ranking.
Q. Is HTTPS really secure?
A. HTTPS encrypts data being exchanged online, so it adds security. However, having HTTPS is not enough. So you can’t solely rely on HTTPS and need to take other precautions to protect the data of your clients. Make sure to partner with a safe web hosting provider, regularly backup your data, and check if you can add any security plugins to your website.
Q. What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
A. The main difference between HTTP and HTTPS is that of data encryption. While HTTP exchanges information over the internet in plain text, HTTPS secures the data by encrypting it so hackers can’t decipher it.
Q. What if we use HTTP in the link instead of HTTPS?
A. Many websites use HTTP, but if you have an eCommerce website or a website that collects and exchanges data of website users, you should prefer HTTPS. Using HTTP can compromise your customer’s data..
Q. How do HTTP and HTTPS work?
A. HTTP and HTTPS are both protocols that help with transmitting information and data online. While HTTP transfers plain text, HTTPS encrypts data while transferring.
Q. What are all the steps to upgrade from HTTP to HTTPS?
A. To upgrade from HTTP to HTTPS, follow these 5 steps:
- Backup all your data
- Plan your migration when your website is not expecting a lot of traffic
- Find the right web host provider to help you migrate your website
- Redirect old website to the new website
- Update all internal links to the HTTPS links
Q. Is HTTPS good for SEO?
A. HTTPS may or may not be good for SEO. But not having HTTPS is bad for SEO. The absence of HTTPS affects the rank of the website better and impacts the traffic on the website as many web browsers prefer websites using HTTPS.
Q. Does change from HTTP to HTTPS affect SEO?
A. Changing from HTTP to HTTPS might affect SEO in the short term
Q. Does HTTP hurt SEO?
A. Web browsers usually prefer HTTPS. SEO ranking can be affected if HTTP is used. Also, if the website uses HTTP, the visitors might not stay on the website, which affects the bounce rate and thus the page authority.
Q. Is using HTTPS a bad SEO practice?
A. Using HTTPS is actually a good SEO practice, as Google officially supports websites using HTTPS. Hence, HTTPS receives more traction leading to a higher conversion rate. So, using HTTPS is not a bad SEO practice but a good SEO practice.




