
cPanel & WHM Explained: Differences, Features, Tools, and Pricing
IT Updated on : December 31, 2025Web hosting can be complex without the right tools. Servers require configuration, accounts need creation, and websites demand ongoing management. This is where cPanel and WHM come in as two complementary control panels that simplify the entire hosting ecosystem.
cPanel and WHM are Linux-based web hosting control panels used to manage websites, servers, email accounts, databases, and hosting users. cPanel is designed for end users to manage individual hosting accounts, while WHM is used by server administrators and hosting providers to manage multiple cPanel accounts on a single server.
cPanel & WHM are widely used by hosting providers, developers, and system administrators worldwide, managing over 50 million domains globally.
In this comprehensive guide, you will learn:
- What are cPanel and WHM, and how do they differ?
- Complete feature breakdowns and tools
- Real-world use cases
- Pricing and licensing information
- Common troubleshooting issues
- Expert answers to frequently asked questions
- cPanel and WHM Explained
What is cPanel?
cPanel is a web-based control panel that allows website owners to manage files, domains, emails, databases, backups, and security settings through a graphical interface without requiring technical expertise.
Developed by J. Nicholas Koston in 1996, cPanel has evolved into the most user-friendly hosting management solution available. It runs exclusively on Linux servers and provides an intuitive dashboard that eliminates the need for command-line expertise.

(Source: cPanel)
Key Characteristics of cPanel:
- Account-level management (individual website)
- End-user focused (website owners, bloggers, small businesses)
- No server-level access required
- Graphical user interface (GUI)
- Linux-exclusive (AlmaLinux, CentOS, RHEL, CloudLinux, Ubuntu)
- Integrated with Apache, Exim, MySQL/MariaDB, BIND/PowerDNS, Dovecot
- Free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificates via AutoSSL
Key cPanel Tools
1. File Manager: The File Manager is your gateway to website file management without requiring FTP knowledge.
What You Can Do:
- Upload, download, edit, delete, move, and copy files
- Create folders and manage directory structure
- Set file permissions (chmod)
- Compress and extract archives (ZIP, TAR, GZIP)
- Search files within your hosting account
Use Case: Website designers uploading custom themes, developers managing source code, bloggers updating website content.
2. Email Accounts: Manage professional email for your domain without mail server expertise.
What You Can Do:
- Create and manage email accounts
- Set mailbox storage limits
- Configure forwarders and autoresponders
- Access webmail interfaces
- Apply spam filtering and email authentication (SPF, DKIM)
Use Case: Small business owners managing customer support emails, entrepreneurs setting up professional email addresses, teams coordinating through shared mailboxes.
3. MySQL Databases: Store and manage website data with integrated database tools.
What You Can Do:
- Create and delete MySQL/MariaDB databases
- Add database users and assign permissions
- Change database credentials
- Monitor database size
- Access databases via phpMyAdmin
Use Case: WordPress installations (each site has a database), e-commerce stores managing product catalogs, and custom applications storing user data.
4. PhpMyAdmin: Advanced database management tool integrated directly into cPanel.
What You Can Do:
- Browse and edit database tables
- Run SQL queries
- Import and export databases
- Manage database users and privileges
- Perform basic database maintenance
Use Case: Developers customizing database structures, database administrators performing maintenance, and teams migrating databases between servers.
5. Domain & Subdomain Management: Manage multiple domains and create professional subdomains from a single account.
What You Can Do:
- Add addon domains and subdomains
- Configure domain redirects
- Manage parked (alias) domains
- Edit DNS records using Zone Editor
- Force HTTPS for domains
Use Case: Portfolio designers hosting multiple client sites, entrepreneurs running several businesses, and agencies managing project-specific domains.
6. SSL/TLS Manager: Secure your website with free or commercial SSL certificates.
What You Can Do:
- Enable free SSL via AutoSSL (Let’s Encrypt)
- Install third-party SSL certificates
- Manage SSL for domains and subdomains
- View certificate status and expiration
- Enforce HTTPS connections
Use Case: E-commerce sites protecting customer payment data (PCI compliance), blogs requiring HTTPS for SEO, and regulated industries requiring encryption.
7. Backup & Restore: Protect your entire account with automated and manual backups.
What You Can Do:
- Generate full or partial backups
- Download backups locally
- Restore files, databases, or email data
- Use the Backup Wizard for guided recovery
- Monitor backup availability
Use Case: Disaster recovery after hackers or malware, accidental file deletion recovery, website testing before major updates, and compliance backup requirements.
8. Metrics & Analytics: Monitor your website performance and resource usage.
What You Can Do:
- View visitor and bandwidth statistics
- Monitor disk usage and resource limits
- Access error logs
- Review domain-level metrics
- Check server status indicators
Use Case: Website owners optimizing for traffic spikes, bloggers tracking audience growth, e-commerce sites monitoring performance during sales.
What Is WHM (Web Host Manager)?
WHM (Web Host Manager) is a server-level control panel used by hosting providers and administrators to create, manage, and control multiple cPanel accounts on a single server.
WHM is the administrative backbone of hosting infrastructure. While cPanel manages individual accounts, WHM orchestrates the entire server, managing resources, creating customer accounts, configuring services, and maintaining security. Only root administrators have access to WHM; it’s not available to regular website owners.
Source: HostRocket
Key Characteristics of WHM:
- Server-level management (entire server and all accounts)
- Administrator and hosting provider focused
- Complete system control and oversight
- Root-level access required
- Linux-exclusive (same OS as cPanel)
- Manages all server services (Apache, PHP, MySQL, Exim, DNS)
- Integrated account and billing management
- Advanced security and monitoring capabilities
Key WHM Tools:
1. Account Creation & Management: Create and manage multiple customer hosting accounts from a single interface.
What You Can Do:
- Create, modify, suspend, or terminate accounts
- Assign disk space and bandwidth limits
- Reset account passwords
- View account usage and status
- Convert addon domains into separate accounts
Use Case: Hosting companies managing 100+ customer accounts, enforcing resource policies, and handling customer onboarding/offboarding.
2. Package Management: Design hosting plans with specific features and resource limits.
What You Can Do:
- Create and edit hosting packages
- Define feature availability and limits
- Assign packages to accounts
- Manage feature lists
- Control reseller package permissions
Use Case: Hosting businesses offering tiered plans, resellers creating packages for their customers, providers scaling infrastructure.
3. Server Monitoring: Monitor server health, resources, and performance in real-time.
What You Can Do:
- View CPU, memory, and disk usage
- Monitor service status (Apache, MySQL, Mail)
- Check running processes
- Track system load averages
- Identify resource bottlenecks
Use Case: Proactive server management, identifying performance issues before customer impact, and capacity planning.
4. DNS Zone Manager: Manage domain DNS records server-wide.
What You Can Do:
- Create and edit DNS zones
- Manage A, MX, CNAME, TXT, and NS records
- Configure email authentication records
- Set TTL values
- Manage nameserver configurations
Use Case: Managing DNS for thousands of domains, implementing email security standards, and scaling nameserver infrastructure.
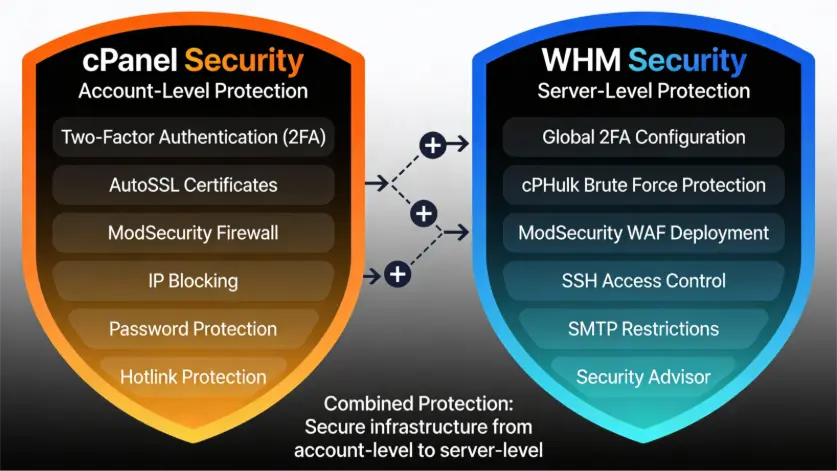
5. Security Center: Implement server-wide security policies and protections.
What You Can Do:
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Configure brute-force protection
- Deploy web application firewall (ModSecurity)
- Control SSH and shell access
- Monitor security advisories
Use Case: Preventing server-wide attacks, protecting against DDoS, enforcing company security policies, and preventing account compromise.
6. Backup Configuration: Set up server-wide automated backup systems.
What You Can Do:
- Schedule automated backups
- Select backup storage locations
- Restore full accounts or individual data
- Monitor backup completion status
- Configure backup retention policies
Use Case: Disaster recovery from server failures, ransomware recovery, planned server migration, and compliance backup requirements.
7. Reseller Management: Empower resellers to manage their own customer accounts.
What You Can Do:
- Create and manage reseller accounts
- Assign limited WHM privileges
- Allocate resources to resellers
- Monitor reseller usage
- Suspend or terminate reseller access
Use Case: Hosting partnerships, white-label reseller programs, multi-tier hosting businesses.
Security Comparison
Differences Between cPanel and WHM
The primary difference between cPanel and WHM is the level of access and scope of control. cPanel is account-level software for individual website owners, while WHM is server-level software for administrators managing entire servers and multiple accounts.
| Aspect | cPanel | WHM |
| Target Users | Website owners, bloggers, small businesses | Server admins, hosting providers, resellers |
| Scope | Individual hosting account | Entire server + all accounts |
| Number per Server | Multiple (one per account) | 1 root + multiple resellers |
| File Access | Own website files only | All server files across all accounts |
| Email Management | Create personal email accounts | Monitor/manage email system server-wide |
| Databases | Create own databases | Manage all databases and repair/upgrade |
| Security | Personal 2FA, personal SSL | Global security policies for all users |
| Accounts | Manage own account only | Create, modify, suspend, terminate ANY account |
| Backups | Personal backups only | Server-wide backup configuration |
| DNS | Edit own domain DNS | Manage all server DNS zones and clusters |
| Monitoring | Own account statistics | All accounts, server health, resources |
| Learning Curve | Easy – user-friendly | Advanced – requires admin knowledge |
cPanel & WHM Features (Detailed Breakdown)
cPanel Features
cPanel offers eight core suites for account-level management.
- File Management – Upload, edit, organize, compress, and manage website files with drag-and-drop functionality and permission controls.
- Email Management – Create professional email accounts with forwarders, autoresponders, spam filters, webmail access, and DKIM/SPF authentication.
- Domain Management – Host multiple domains, create subdomains, manage redirects, edit DNS records, and force HTTPS.
- Database Management – Create MySQL/MariaDB databases, manage users, access phpMyAdmin, and run SQL queries directly.
- Application Installation (Softaculous) – One-click installation of WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, ecommerce platforms, forums, and galleries with automatic updates.
- Security Management – Enable AutoSSL (free Let’s Encrypt), 2FA, IP blocking, password-protected directories, ModSecurity firewall, and WordPress security scanning.
- Backup & Restore – Create full or partial backups, schedule automated backups, store remotely, and restore files or databases with one click.
- Metrics & Analytics – Monitor visitor statistics, bandwidth usage, resource limits, error logs, and performance trends.
WHM Features
WHM provides 13 major administration suites for server-level control.
- Account Management – Create, modify, suspend, and terminate cPanel accounts. Reset passwords, assign IPs, set resource limits, and batch-manage multiple accounts.
- Package Management – Design hosting plans with custom features, resource limits, pricing tiers, and reseller-specific packages.
- Server Monitoring – Monitor CPU, memory, disk space, daemon statuses, running processes, bandwidth, email queue, and database performance in real-time.
- DNS Administration – Create and manage DNS zones, configure MX/DKIM/SPF/DMARC records, set TTL values, manage DNS clusters, and troubleshoot propagation.
- Service Management – Control Apache, PHP (MultiPHP), Exim mail server, DNS, MySQL, FTP, and service SSL certificates. Configure automatic restarts and performance tuning.
- Database Administration – Manage MySQL, MariaDB, and PostgreSQL globally. Reset passwords, repair tables, upgrade versions, monitor performance, and configure remote access.
- Server-Wide Security – Enable global 2FA, configure brute force protection (cPHulk), deploy ModSecurity WAF, control SSH access, restrict SMTP, and monitor alerts.
- Backup Systems – Configure automated backups, select storage location (local/remote), include/exclude accounts, verify integrity, and transfer accounts via cpmove.
- Reseller Management – Create reseller accounts with limited privileges, assign IPs, delegate nameserver access, monitor resource usage, and manage reseller accounts.
- Software & System Management – Update packages, manage multiple PHP versions (MultiPHP), install modules (PHP, Perl, Ruby), upgrade databases, and apply security patches.
- Email Administration – Manage mail queues, configure SpamAssassin and greylisting, set up DKIM/SPF/DMARC globally, repair mailboxes, and track email statistics.
- SSL/TLS Management – Deploy AutoSSL globally, manage Let’s Encrypt automation, install commercial certificates, generate CSRs, and handle multi-domain SSL.
- IP Management – Manage IPv4 and IPv6 pools, assign IPs to accounts, migrate between servers, reserve IPs, and configure nameserver IPs.
Benefits of Using cPanel and WHM Together
- Centralized server and website management – Single dashboard for all operations
- Easy scalability for hosting businesses – Add accounts and resellers without infrastructure changes
- Enhanced security controls – Global security policies + account-level protection
- Faster website deployment – One-click application installation across all accounts
- Simplified backups and restorations – Automated server-wide and account-level backups
- Multi-user access levels – Root, reseller, and customer tiers with appropriate permissions
- Reduced operational complexity – Eliminate multiple tools and integrate everything into one platform
- Cost-effective infrastructure management – Run thousands of accounts on a single server
- Automated email management – Centralized configuration with per-account customization
- Automated certificate management – Let’s Encrypt SSL for all domains automatically
- Professional appearance – Branded control panel for customers and resellers
- Industry standard support – Extensive documentation and community assistance
cPanel and WHM Use Cases
Use Case 1: Freelance Web Designer
Scenario: Designer hosts 15 client websites on shared hosting
How They Use It:
- Log in to cPanel for each client site
- Upload custom website files via File Manager
- Create and configure email accounts for clients
- Install WordPress or other CMS via Softaculous
- Configure SSL certificates via AutoSSL
- Set up backups for client website protection
- Monitor website traffic and performance
Benefits: Manage multiple clients without server knowledge, professional website deployment, and client security.
Use Case 2: Small Business Owner
Scenario: Restaurant runs website, email, and online ordering system
How They Use It:
- Upload menu and website updates via File Manager
- Create professional email accounts (@restaurant.com)
- Set up email forwarders for team members
- Install WordPress for the blog and news
- Configure SSL for online ordering security
- Schedule automatic backups for peace of mind
- Monitor website traffic during promotions
Benefits: Professional online presence, business communication, payment processing security, and disaster recovery.
Use Case 3: Hosting Reseller
Scenario: A Web designer runs a reseller hosting business with 50 clients
How They Use It:
- Root admin creates reseller account via WHM
- Reseller uses limited WHM to create customer accounts
- Reseller designs hosting packages for different client types
- Each client receives a cPanel login for their account
- Reseller monitors client usage and bandwidth
- Root admin manages global server settings
- Both use WHM for different administrative tiers
Benefits: White-label service offering, scalable business model, customer self-service, and infrastructure leverage.
Use Case 4: Hosting Provider
Scenario: Company hosts 500+ websites on multiple servers
How They Use It:
- Root admin manages server infrastructure via WHM
- Create hosting packages (Basic, Business, Enterprise)
- Manage 500+ customer accounts and resource allocation
- Multiple resellers use limited WHM for their customers
- Global security policies and monitoring
- Automated backups across all servers
- Central DNS management for all domains
- Monitoring and alerting for server health
Benefits: Scalable infrastructure, customer management, resource efficiency, and centralized administration.
Use Case 5: Agency with Multiple Departments
Scenario: Digital agency with design, development, and support teams
How They Use It:
- Designers manage website files and upload
- Developers configure databases and applications
- Support team handles email and customer issues
- Project managers monitor website performance
- All teams have access to different cPanel features per role
- WHM admin manages the overall infrastructure
Benefits: Role-based access control, team collaboration, specialized responsibilities, and security through permissions.
cPanel and WHM Pricing & Licensing (Overview)
Is cPanel & WHM Free?
No. cPanel & WHM require licensing from cPanel, LLC, but costs are typically included in your hosting fee ($5-15/month for shared hosting, $10-50/month for VPS).
Pricing Structure
cPanel uses per-server licensing based on account count:
| Accounts | Monthly Cost |
| 1 | $29.99/mo |
| Up to 5 | $35.99/mo |
| Up to 30 | $53.99/mo |
| Up to 100 | $69.99/mo |
Note: Pricing varies by hosting provider, region, and licensing agreement.
What Affects Pricing?
- Number of accounts
- Server type (Shared, VPS, Dedicated)
- Hosting provider rates
- Geographic region
- Add-ons & plugins
- Volume discounts
Can I Use cPanel and WHM Without Paying?
No, you cannot use cPanel & WHM for free on a long-term basis because it requires a paid license. But on a new installation, you will have a 15-day free trial for testing purposes. Once the trial period ends, you must buy a license either directly from the cPanel Store or from your hosting provider to keep using it.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
cPanel-Related Issues
Issue 1: Can’t Upload Files to File Manager
Possible Causes:
- File size exceeding limits
- Insufficient disk space quota
- File permissions are not allowing upload
- FTP daemon issues
Solutions:
- Compress files before uploading
- Check disk quota usage in cPanel metrics
- Use FTP client (FileZilla) as an alternative
- Check file permissions (chmod settings)
- Contact the hosting provider if the issue persists
Issue 2: Email Not Receiving Messages
Possible Causes:
- Email quota exceeded
- SPF/DKIM records are misconfigured
- Email forwarder issues
- Mail server problems
Solutions:
- Check the email account quota in cPanel
- Verify SPF and DKIM records in Email Authentication
- Review email forwarder settings
- Check the spam folder for messages
- Review mail queue status
- Contact the hosting provider if persistent
Issue 3: Database Connection Failed
Possible Causes:
- Incorrect database credentials
- Database user permissions
- MySQL server offline
- Firewall blocking connections
Solutions:
- Verify database username and password
- Check database user permissions in phpMyAdmin
- Verify the database server is running
- Check remote database access settings
- Restart MySQL service (via hosting provider)
Issue 4: SSL Certificate Not Installing
Possible Causes:
- AutoSSL not running
- Domain DNS is not pointing to the server
- Certificate already installed
- Domain validation issues
Solutions:
- Wait for AutoSSL to process (24-48 hours)
- Verify the domain DNS A record points to the server IP
- Check the SSL Storage Manager for the existing certificate
- Verify domain ownership in DNS
- Manually request a certificate in SSL Manager
WHM-Related Issues
Issue 1: Account Creation Fails
Possible Causes:
- Insufficient disk space
- IP address unavailable
- Account quota exceeded
- MySQL service issues
Solutions:
- Check server disk space availability
- Verify available IP addresses in IP Manager
- Check total account count vs license limit
- Verify the MySQL service is running
- Check account creation logs for specific errors
Issue 2: DNS Not Resolving
Possible Causes:
- DNS zone configuration errors
- Nameserver not responding
- BIND service offline
- Incorrect DNS records
Solutions:
- Verify the DNS zone exists in the DNS Zone Manager
- Check the BIND service status
- Verify nameserver A records
- Use the external DNS checker tool
- Restart the BIND service from the Service Manager
Issue 3: High Server CPU Usage
Possible Causes:
- Runaway processes
- Email queue backup
- Database queries
- Traffic spike
Solutions:
- Monitor processes via Server Status
- Kill runaway processes in Process Manager
- Check email queue status
- Monitor database performance
- Review Apache connections and processes
- Identify resource-heavy accounts
Issue 4: Backup Fails
Possible Causes:
- Insufficient storage space
- Network connectivity issues
- Account too large
- Backup service offline
Solutions:
- Check available disk space
- Verify remote storage connectivity (FTP)
- Enable partial backups for large accounts
- Check backup service logs
- Restart the backup service
- Configure smaller backup increments
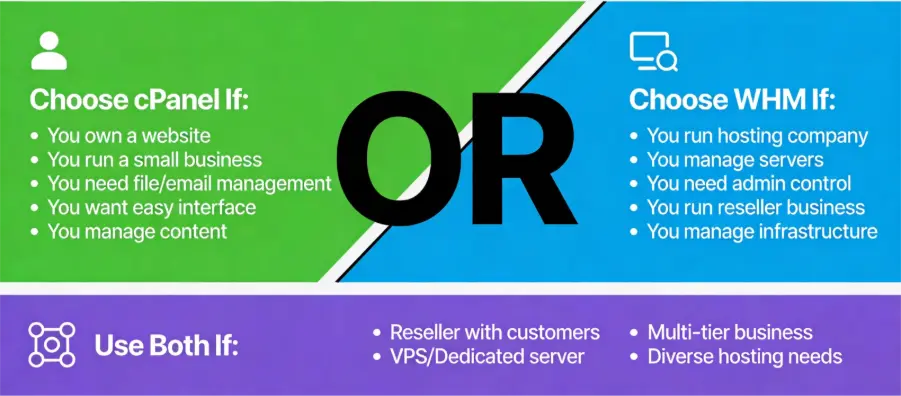
Quick Overview of Which One Should You Choose?
cPanel & WHM Alternatives in 2026
While cPanel and WHM dominate the market, several alternatives exist for hosting management:
| If You Need | Best Alternatives |
| Windows support | Plesk |
| Lower reseller cost | DirectAdmin |
| Maximum WordPress performance | CyberPanel |
| Developer flexibility (free) | aaPanel |
| Minimal resource usage (free) | HestiaCP |
| High-performance cloud hosting | CloudPanel |
| Advanced customization | Webmin / Virtualmin, ISPConfig |
1. Plesk: The leading enterprise-level alternative to cPanel & WHM. It remains the only major control panel that fully supports both Linux and Windows servers. In 2026, its WordPress Toolkit continues to set the benchmark for features such as staging, cloning, and security hardening.
2. DirectAdmin: Ideal for budget-focused hosting providers and resellers. Unlike cPanel, it uses a flat-rate licensing model that often allows unlimited accounts, making costs far more predictable as businesses grow. It is also well known for running efficiently on smaller VPS configurations.
3. CyberPanel & CloudPanel:
- CyberPanel: Built on OpenLiteSpeed, it delivers strong performance for WordPress and other PHP-based websites.
- CloudPanel: Designed specifically for cloud platforms such as AWS and DigitalOcean, with a strong emphasis on speed and performance. While exceptionally fast, it traditionally omits built-in email and DNS management to focus purely on website performance.
4. aaPanel: A widely used free and open-source control panel in 2026, especially popular among developers. It offers a modular, app-store-style interface that enables one-click installation of services like Nginx, Apache, and multiple PHP versions.
5. Open-Source Veterans:
- HestiaCP: Remains a top choice for users seeking a free, lightweight control panel (around 200MB RAM) that still includes a full email stack.
- Webmin/Virtualmin & ISPConfig: Favored by experienced system administrators who require deep customization and multi-server management, though they come with a steeper learning curve compared to cPanel.
Conclusion
cPanel and WHM are the industry standard for web hosting management, powering 50+ million domains. Their almost 28-year track record, extensive documentation, and user-friendly interfaces have established them as the preferred choice for hosting professionals worldwide.
- For website owners and small businesses: cPanel simplifies website management with one-click installers, automated SSL certificates, email management, and backup tools – no technical expertise required.
- For hosting providers and administrators: WHM provides complete server control, multi-account management, global security policies, and reseller functionality for building scalable hosting businesses.
Whether launching your first website, migrating hosting, or building a hosting business, cPanel and WHM provide the tools and infrastructure needed for success. Explore your hosting control panel today and leverage your provider’s documentation and support to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is cPanel beginner-friendly?
Ans. Yes, cPanel is designed for non-technical users with an intuitive interface.
Q2. Can I install WordPress via cPanel?
Ans. Yes, most cPanel setups include one-click WordPress installers.
Q3 Do I need WHM for shared hosting?
Ans. No, shared hosting users typically only need cPanel.
Q4. Are cPanel and WHM secure?
Ans. Yes, they include built-in security tools and regular updates.
Q5. Can I migrate websites using cPanel and WHM?
Ans. Yes, both offer tools for backups and account migrations.
Q6. What are cPanel and WHM used for?
Ans. cPanel is for website owners managing individual hosting accounts (files, email, databases, backups, security). WHM is for hosting providers managing multiple cPanel accounts and server infrastructure.
Q7. Who should use cPanel?
Ans. Website owners, bloggers, small business operators, and individuals managing their own hosting accounts.
Q8. What operating systems support cPanel?
Ans. cPanel runs on Linux (AlmaLinux, CentOS, RHEL, CloudLinux, Ubuntu). Windows Server is not supported.
Q9. Can I use cPanel without WHM?
Ans. Yes, End users use only cPanel. WHM is only for server administrators.
Q10. How many accounts can cPanel handle?
Ans. There’s no technical limit, but practical limits depend on server resources (typically 50-500 accounts for shared hosting).




